Introduction
Few have transformed wealth management like Charles R. Schwab. He broke down barriers that made investing exclusive and costly. Through The Charles Schwab Corporation, he created affordable, transparent brokerage services. His innovations empowered everyone. People to participate confidently in the stock market.In the mid-20th century, brokerage firms charged fixed, high commissions. Investing was expensive and largely limited to the wealthy. This system restricted broader participation and slowed economic inclusion.
Schwab changed that model. He introduced lower-cost, transparent brokerage services focused on everyday investors. What began as a simple newsletter business evolved into a diversified financial powerhouse built on technology and customer-first thinking.
Today, The Charles Schwab Corporation manages trillions in client assets. Its success reflects the strength of Schwab’s original vision: affordable, accessible investing for all. His innovations continue to influence modern fintech and inspire new generations of entrepreneurs.
Quick facts
- Full name: Charles Robert Schwab Sr.
- Born: July 29, 1937 Sacramento, California, U.S.
- Known for: Founder of The Charles Schwab Corporation; pioneer of discount brokerage.
- Education: BA (Economics), MBA Stanford University.
- Company assets (2026): ~$11.9 trillion in total client assets.
- Estimated net worth (Jan 2026): ~$13.5 billion (Forbes estimate).
Early life & education
Birth and family background
Charles Robert Schwab Sr. entered the world on July 29, 1937, in the bustling city of Sacramento, California, USA. Raised in a typical middle-income household, young Charles was immersed in an environment that valued diligence and curiosity. His parents, though not wealthy, sparked his early interest in money and economics.As a child, he was curious about how money moved and how markets worked.He often experimented with saving and trading his pocket money.Family stories recall his early fascination with financial concepts.These experiences laid the foundation for his future in investing and finance.
This foundational curiosity, nurtured amid the post-Depression recovery era, laid the groundwork for his future endeavors in the investment realm. Sacramento’s vibrant community, with its mix of agricultural roots and emerging urban opportunities, provided a fertile backdrop for his developing worldview, emphasizing self-reliance and innovative thinking.
His family’s modest circumstances taught him resilience, as they navigated the challenges of wartime rationing and post-war booms. These experiences weren’t mere anecdotes; they shaped his empathy for ordinary folks striving to secure their financial futures.
Stanford MBA: Building the Foundation for Financial Innovation
Charles Schwab went on to earn an MBA from Stanford Graduate School of Business.The program strengthened his skills in corporate finance and management.He studied investment strategies and real-world business case studies.Stanford emphasized ethical leadership and innovation, which shaped his approach.This education prepared him to launch disruptive ideas in the brokerage industry.
This advanced education delved deeper into corporate finance, management strategies, and investment analysis, equipping him with the expertise to navigate complex business landscapes. The MBA program emphasized practical applications, including case studies on real-world financial dilemmas, which resonated with his innate problem-solving abilities. Graduates from Stanford’s business school often credit the program’s emphasis on ethical leadership and innovation, qualities that Charles Schwab exemplified throughout his career. This educational attainment not only armed him with technical knowledge but also cultivated a visionary perspective, enabling him to envision and execute disruptive models in the brokerage industry. In essence, his time at Stanford transformed raw curiosity into a professional toolkit, setting the stage for groundbreaking contributions to finance.
First steps: Investment Indicator and early career
Upon completing his MBA, Charles Schwab embarked on his professional odyssey by initiating a modest venture in publishing and advisory services known as the Investment Indicator, a periodical newsletter co-launched with collaborators. This publication served as an educational resource, disseminating insights on market trends, stock selections, and investment strategies to a niche audience. Within a short span, it garnered several thousand subscribers, validating the demand for straightforward, cost-effective guidance in the investment sphere. Through this endeavor, Charles Schwab gained invaluable lessons in audience engagement and the art of simplifying complex financial concepts, themes that would permeate his subsequent business models. The newsletter’s success highlighted a critical gap in the market: the need for accessible information that empowered novice investors without overwhelming them with jargon.
The Investment Indicator: Where Charles Schwab’s Vision Began
This early project was more than a financial stepping stone; it was a crucible for refining Charles Schwab‘s entrepreneurial instincts. By interacting directly with subscribers through feedback and queries, he discerned the frustrations many faced with traditional brokerage services high costs, limited transparency, and inadequate education. These interactions fueled his resolve to bridge these gaps, transforming anecdotal insights into actionable strategies. The Investment Indicator also introduced him to the intricacies of regulatory environments and content distribution, skills that proved pivotal in scaling operations later on. In the broader narrative of his career, this phase represents the germination of ideas that challenged industry norms, emphasizing education as a cornerstone of financial empowerment. Charles Schwab‘s ability to pivot from academia to practical application underscores his adaptability, a trait that defined his trajectory from advisor to industry disruptor.
Moreover, the collaborative nature of the Investment Indicator project honed Charles Schwab‘s leadership style, fostering partnerships that balanced diverse expertise. As subscriptions grew, so did his understanding of scalable content delivery, foreshadowing the technological integrations that would characterize his brokerage firm. This period, though nascent, was instrumental in building credibility and a loyal following, elements that transitioned seamlessly into his brokerage inception. Reflecting on these initial forays, it’s evident how they cultivated a customer-first mentality, ensuring that future innovations were rooted in real-world needs rather than abstract theories. Thus, the Investment Indicator stands as a testament to Charles Schwab‘s foresight in recognizing that informed investors are the bedrock of a healthy financial ecosystem.
Founding Charles Schwab & Co. and pioneering discount brokerage
Founding (1971)
In 1971, Charles Schwab, alongside strategic partners, established a brokerage entity initially named First Commander Corporation, which evolved into the iconic Charles Schwab & Co. This formation marked a deliberate fusion of informational publishing with transactional services, crafting a brand synonymous with investor enlightenment and accessibility. From its inception, the firm prioritized educational resources, offering seminars, guides, and personalized advice to demystify investing for the masses. Charles Schwab‘s vision was to create a holistic platform where knowledge and action converged, addressing the informational asymmetries that plagued traditional brokerages. This foundational step not only launched his eponymous enterprise but also set a precedent for integrating advisory and execution services under one roof.
The early years of Charles Schwab & Co. were characterized by organic growth, driven by word-of-mouth endorsements and a commitment to integrity. Charles Schwab personally oversaw operations, ensuring that every client interaction aligned with his ethos of transparency. By blending his newsletter expertise with brokerage functionalities, the company quickly differentiated itself in a crowded market. This period saw the development of proprietary tools for portfolio tracking and market analysis, tailored for individual users rather than institutional behemoths. The founding narrative illustrates Charles Schwab‘s strategic acumen in leveraging synergies between content and commerce, laying a robust infrastructure for exponential expansion.
The big idea: discount brokerage (1975)
The pivotal moment arrived in 1975 when regulatory deregulation permitted brokerages to determine their own fee structures, unshackling the industry from fixed commissions. Charles Schwab astutely capitalized on this shift by unveiling a discount brokerage paradigm, slashing trading costs dramatically and making stock transactions viable for average households. This model eliminated the premium surcharges that had long deterred small-scale investors, ushering in an era of retail revolution. By offering fixed, low-rate executions without compromising on service quality, Charles Schwab challenged entrenched players, forcing a reevaluation of pricing norms across the sector.
This innovation was revolutionary because it aligned with broader economic democratization trends, enabling wage earners to participate actively in wealth creation. Charles Schwab‘s discount approach wasn’t merely about cost reduction; it was about fostering confidence through affordability, coupled with robust support systems. Clients could now execute trades with minimal friction, supported by educational materials that enhanced decision-making. The immediate uptake demonstrated the model’s viability, as account openings surged, validating Charles Schwab‘s hypothesis that accessibility breeds participation.
Why this mattered
The essence of this breakthrough can be encapsulated as: reduced expenses plus transparent guidance equals broader investment engagement. When transaction fees no longer devour potential returns, saving and growing wealth becomes a practical pursuit for everyday individuals. Charles Schwab‘s model transformed investing from a privilege to a possibility, catalyzing a surge in market liquidity and economic inclusivity. In practical terms, it meant that a teacher or mechanic could now afford to diversify their portfolio without prohibitive barriers, a shift that rippled through society, promoting financial independence on a massive scale.
Major innovations and growth (1975–2000)
Using technology early
Charles Schwab was a trailblazer in harnessing technological advancements to enhance user experiences within the financial domain. In the 1980s, his firm pioneered round-the-clock telephone-based market quotations, allowing clients to access real-time data at their convenience, irrespective of traditional business hours. This innovation bridged the gap between market volatility and investor responsiveness, empowering users to make timely decisions. As digital paradigms evolved, Charles Schwab swiftly transitioned to internet-enabled trading platforms, introducing web-based interfaces that streamlined order placements and research compilations. These tools democratized advanced analytics, previously reserved for professionals, making sophisticated strategies available to novices.
The adoption of technology under Charles Schwab‘s guidance wasn’t opportunistic; it was visionary, anticipating the digital revolution’s impact on finance. By investing in user-friendly software, the company reduced operational overheads while elevating service efficiency. For instance, early online portals featured intuitive dashboards for portfolio monitoring, educational videos, and simulated trading environments, fostering a learning curve for beginners. This proactive stance positioned The Charles Schwab Corporation as a leader in fintech, influencing competitors to accelerate their own digital transformations. The ripple effects included heightened client retention and acquisition, as technology became a competitive differentiator in an increasingly connected world.
Going public and expansion
The landmark event of 1987 saw The Charles Schwab Corporation debut on public markets through an initial public offering (IPO), injecting capital for aggressive scaling. This move facilitated diversification into ancillary services such as mutual fund supermarkets, retirement planning vehicles like IRAs, and comprehensive wealth advisory offerings. Beyond core brokerage, the firm ventured into banking solutions and holistic financial planning, creating an ecosystem where clients could consolidate their monetary affairs seamlessly. Charles Schwab‘s strategic expansions were methodical, targeting underserved segments like self-directed investors seeking low-cost alternatives.
Post-IPO growth was meteoric, with branch networks proliferating across the U.S. and international outposts emerging to tap global markets. The company’s ethos of innovation persisted, introducing automated investment advisors and robo-advisory precursors that personalized recommendations based on user profiles. These developments not only bolstered revenue streams but also reinforced Charles Schwab‘s reputation as an adaptive powerhouse. By the turn of the millennium, the firm had evolved from a discount broker into a full-service financial conglomerate, serving diverse clientele from retail enthusiasts to high-net-worth individuals.
Later leadership, role changes, and the company today (2000–2026)
Leadership changes
Throughout the 2000s, Charles Schwab navigated multiple Leadership incarnations, serving as chief executive officer during key intervals from 1986 to 1997 and again from 2004 to 2008. These tenures were marked by steering the company through market upheavals, including the dot-com bust and the 2008 financial crisis, where his steady hand preserved stability and client trust. Subsequently, he transitioned to chairman and co-chairman positions, facilitating a professionalization of management layers while retaining influence as a symbolic ambassador for investor empowerment. Even in semi-retirement, Charles Schwab remained a vocal advocate, authoring publications and delivering speeches that underscored the company’s foundational values.
This evolution in roles reflected Charles Schwab‘s maturity as a leader, prioritizing succession planning to ensure sustainability.
Company scale by 2025–2026
By late 2026, Charles Schwab Corporation managed about $11.9 trillion in client holdings and over 46 million accounts.
This made it one of the world’s leading investment service providers.Official reports and media coverage highlight its vast reach and efficiency.Mergers, including the TD Ameritrade acquisition, fueled its growth.These moves expanded platforms, clients, and service offerings globally.
This scale underscores Charles Schwab‘s enduring impact, as the company now caters to a spectrum of users from individual savers to institutional entities. The asset management figures reflect not just quantitative dominance but qualitative excellence in client satisfaction and product innovation.
Recent performance
In early January 2026, The Charles Schwab Corporation announced exceptional fiscal outcomes for the fourth quarter and full year of 2026, showcasing unprecedented revenue escalation, robust interest earnings, and vibrant trading volumes. Net revenues climbed to $6.34 billion for the quarter, marking a 19% increase from the prior year, while net profits soared to $2.46 billion. The year also witnessed substantial inflows of fresh assets, demonstrating the firm’s magnetic appeal to new patrons amid competitive landscapes. These results, disseminated via official channels, affirm the company’s resilience and strategic agility in navigating economic currents.
The performance narrative reveals Charles Schwab‘s legacy in action, as diversified revenue sources from trading commissions to advisory fees, sustained profitability. Analysts praised the integration of AI-driven tools and personalized services as key drivers, ensuring the firm remains at the vanguard of financial services evolution.
Net worth, company size, and recent performance
Personal net worth
As per Forbes’ January 2026 valuation, Charles R. Schwab‘s personal fortune is appraised at approximately $13.5 billion, accrued primarily through equity holdings in The Charles Schwab Corporation, dividend distributions, and proceeds from historical stock dispositions. This wealth accumulation mirrors his pivotal role in scaling the enterprise from a startup to a multibillion-dollar entity, with ongoing stakes ensuring alignment with company fortunes. Fluctuations in net worth estimates often correlate with market valuations and corporate milestones, yet Charles Schwab‘s financial stature remains a testament to sustained value creation.
Beyond monetary figures, his net worth encapsulates intangible assets like brand influence and philanthropic endeavors, which enhance his legacy. Philanthropic commitments, including substantial donations, subtly modulate public perceptions of his wealth, portraying a balanced portrait of affluence and altruism.
Company financial snapshot
| Metric | Value (2026 / Dec 31) |
| Total client assets | ~$11.9 trillion |
| Total client accounts | ~46 million (active + bank accounts) |
| 2026 net revenue (Q4 results reported Jan 21, 2026) | Q4 net revenues $6.34 billion, up 19% YoY |
| Net income (Q4 2026) | Net income rose to $2.46 billion for the quarter |
These indicators delineate The Charles Schwab Corporation‘s operational magnitude and fiscal vitality, with trillion-scale assets signifying vast client trust and market penetration.
Why these numbers matter
Vast asset repositories indicate that Charles Schwab‘s firm serves an immense cohort of individuals and organizations, conferring economies of scale that sustain competitive pricing and diverse offerings. This framework generates revenue via interest margins, investment management charges, and ancillary services, perpetuating a virtuous cycle of growth and accessibility. For the layperson, these metrics translate to reliable, low-barrier entry points into investing, amplifying wealth-building potential across demographics.
Personal life and philanthropy
Family & personal notes
Charles Schwab has enjoyed an enduring union in his second marriage to Helen O’Neill, with whom he shares a close-knit family, including multiple offspring. Domestic life, interspersed with personal adversities, profoundly influenced his dedication to educational advocacy and cognitive development initiatives. These familial dynamics provided a personal lens through which he viewed broader societal needs, particularly in supporting underprivileged learners. His household served as a microcosm of the values he championed professionally—resilience, learning, and communal support.
The interplay between private spheres and public personas in Charles Schwab‘s life highlights how intimate experiences can inform grand-scale philanthropy. Challenges within the family unit, such as health or learning hurdles, galvanized his commitment to causes that resonate personally, ensuring authenticity in his giving.
Dyslexia and education work
Later revelations uncovered that Charles Schwab and a relative grappled with dyslexia, a discovery that catalyzed the establishment of the Charles and Helen Schwab Foundation. This entity champions research and interventions for youth with learning variances, aiming to unlock their innate potentials through tailored programs and advocacy. The foundation’s efforts span grants to educational institutions, policy influencing, and community workshops, fostering inclusive learning environments nationwide.
Charles Schwab‘s personal narrative with dyslexia transformed vulnerability into advocacy strength, emphasizing neurodiversity’s role in innovation. By funding initiatives that address learning barriers, he not only honors his experiences but also contributes to systemic reforms in education.
Community & arts
Charles Schwab has actively engaged with civic and cultural entities, holding positions on museum governance boards and channeling philanthropy toward artistic and scholarly pursuits. His contributions bolster local heritage preservation and creative endeavors, enriching community fabrics. These involvements reflect a holistic approach to giving, extending beyond finance to nurture cultural vitality and intellectual growth.
Through board services and monetary support, Charles Schwab has amplified voices in the arts, ensuring diverse narratives find expression. This multifaceted philanthropy underscores his belief in interconnected societal pillars—education, culture, and economy—as engines of progress.
Legacy: How Charles Schwab changed investing
What changed because of him (short list)
- Reduced trading costs — Charles Schwab‘s discount framework compelled sector-wide fee reductions, rendering investment pursuits more economical for participants.
- Enhanced tool accessibility — From telephonic data feeds to digital applications and mobile interfaces, he provided intuitive apparatuses for transaction execution and strategic planning.
- Emphasis on investor enlightenment — Through authored volumes, periodic dispatches, and multimedia resources, he disseminated foundational knowledge to demystify financial intricacies.
- Integrated financial solutions — Amalgamating brokerage, depository functions, and consultative services into a unified hub streamlined monetary management for users.
These transformations collectively lowered entry thresholds, broadened participation, and elevated overall market efficiency.
A simple example that shows the impact
Envision two professionals, designated as Individual X and Individual Y. Individual X relies on conventional intermediaries, exacting substantial levies and proffering minimal instructional support. Conversely, Individual Y engages Charles Schwab‘s ecosystem: economical charges, virtual platforms, and didactic materials. Across three decades, Individual Y’s augmented yields—stemming from diminished erosions and refined methodologies—could burgeon into substantially augmented retirement reserves. This juxtaposition elucidates the tangible, quotidian metamorphosis Charles Schwab engendered, rendering fiscal autonomy attainable for myriad households.
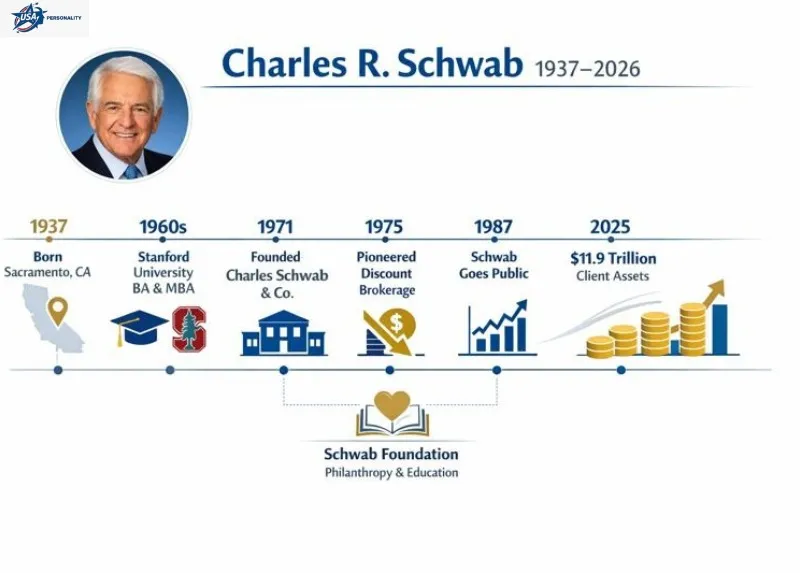
Timeline
| Year | Event |
| 1937 | Born in Sacramento, CA. |
| 1960s | Graduated Stanford (BA, MBA). Initiated financial publishing endeavors. |
| 1963 | Investment Indicator newsletter (inaugural enterprise). |
| 1971 | Founded First Commander Corp. (subsequently Charles Schwab & Co.). |
| 1975 | Commenced discount brokerage provisions. |
| 1987 | Company IPO. |
| 2008 | Relinquished CEO position (partial withdrawal). |
| 2026 | The company attained pinnacle client holdings (~$11.9T). |
| 2026 | Q4 outcomes exhibit unprecedented earnings; Charles Schwab persists as a prominent luminary. |
FAQs
A: He is the founder and long-time leader of The Charles Schwab Corporation, known for making investing cheaper and easier for regular people.
A: He introduced discount brokerage, pushed for user-friendly tools, and emphasized investor education. These moves lowered costs and opened markets to many more people.
A: As of January 2026, Forbes estimates his net worth at about $13.5 billion.
A: By the end of 2026 the company reported roughly $11.9 trillion in total client assets and tens of millions of client accounts.
A: Yes, he has served as chairman or co-chairman and remains a public leader and figurehead for the company’s mission.
Conclusion
Charles R. Schwab’s life is a testament to innovation, perseverance, and the power of financial accessibility. From his early curiosity about money to founding .The Charles Schwab Corporation and pioneering discount brokerage. he reshaped how everyday people invest and manage wealth.
Through his focus on education, technology, and clarity, Schwab lowered barriers to investing, license millions of individuals, and created a zillionaire-dollar Enterprise that continues to thrive decades later. Beyond business, his philanthropy and advocacy for learning differences demonstrate a commitment to improving society, not just markets.
Ultimately, Schwab’s story shows that vision and empathy can transform industries, making complex systems simple and inclusive. His legacy endures in every investor who now has the tools, knowledge, and confidence to build a secure financial future.



